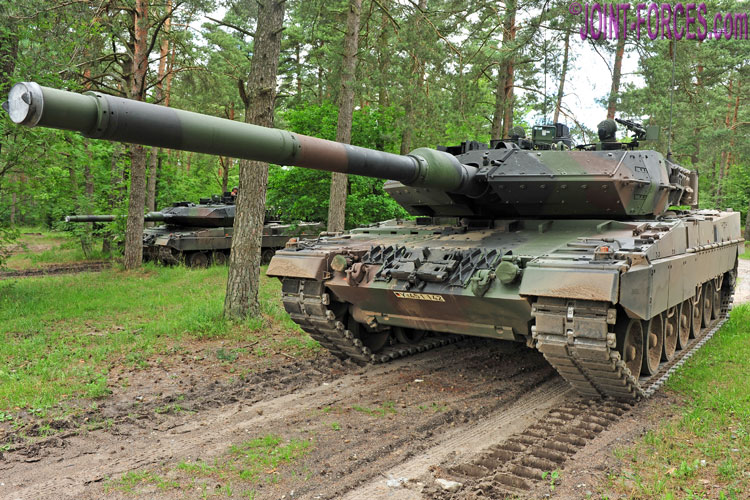

In this new six-part series photojournalist and military historian Carl Schulze looks back at the Bundeswehr Leopard 2 MBT over its 40 year service history.
~
On 24th October 1979, the first series production Leopard 2 main battle tank was officially handed over to the Bundeswehr. Panzer Lehr Bataillon 93, stationed in Munster, was the first unit of the German Army to be equipped with the new combat vehicle from 1st August 1980 onwards. In 2020, forty years later, the Leopard 2, which has since been upgraded several times to increase its combat power, is still the main weapon system of the German Army’s armoured units and, despite its age, is considered one of the best main battle tanks in the world.
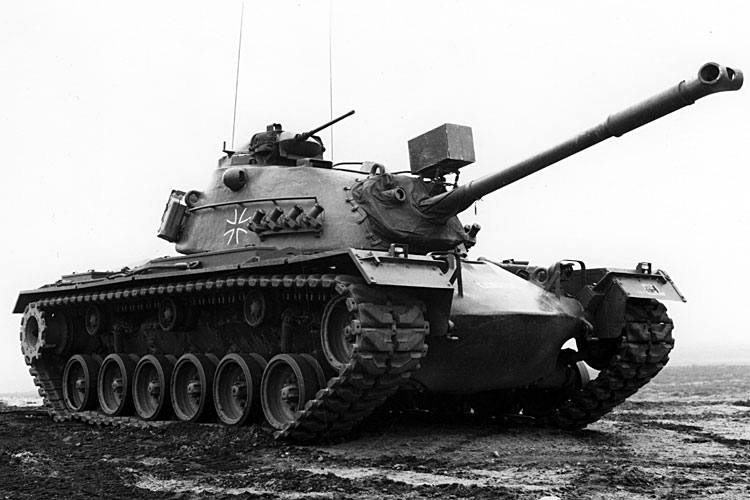

The American-produced M47 from was the first tank fielded by the armoured forces of the German Army, which was newly established in 1955. From 1956 Germany received 1,109 of the vehicles and from 1957 the armoured forces also received 1,692 M48 A1 and M48 A2 main battle tanks. When the M47 and the M48 A1/A2 were introduced it was already clear that these tanks were temporary solutions as they did not sufficiently meet the performance parameters required by the German armoured forces. One problem of these vehicles was the high fuel consumption of their petrol engines, which only allowed a rather limited operational radius. In the case of the M47 another issue was that from the mid-sixties onwards, the supply of spare parts was no longer assured. With the introduction of the Leopard 1 main battle tank from 1965 onwards, the development of which had already begun in 1956, the M47s were gradually withdrawn from service as part of a half-generation changeover. By 1976, the Bundeswehr had received a total of 2,437 Leopard 1 in various versions.
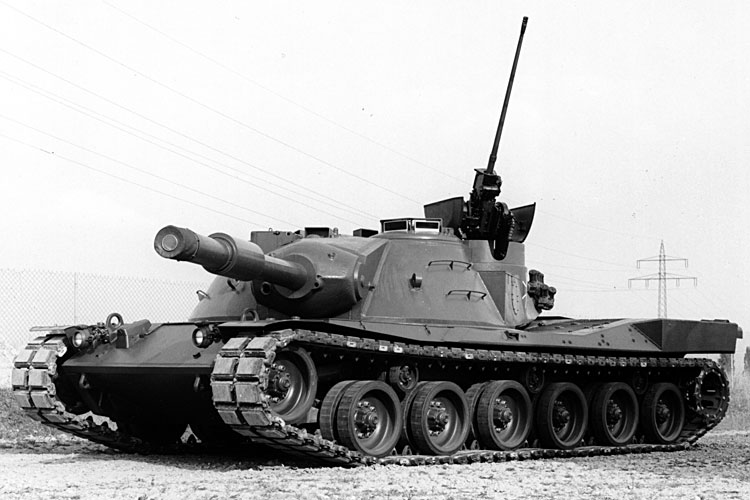

Kampfpanzer 70 / Main Battle Tank 70
The M48 A1 and M48 A2 were intended to be replaced by a super-modern main battle tank developed jointly by the United States of America and the Federal Republic of Germany. Development of the vehicle designated Kampfpanzer 70 / Main Battle Tank 70 (MBT 70) began in 1963.
Among other things, the tank was to: have a combat weight of 50 tons and a three-man crew; be able to shoot while on the move; be equipped with primary stabilised optics that would be tracked by the main weapon; be capable of night combat; have a laser range finder and a main weapon, capable of firing both conventional tank ammunition and guided missiles; be equipped with a height-adjustable hydro-pneumatic running gear; have welded spaced armour; be equipped with NBC protection and air-conditioning; be fitted with an automatic loader for the main weapon and; have a 20 mm automatic cannon as a secondary weapon which could be aimed independently of the main weapon.
However, after the construction of ten prototypes, the development project was officially cancelled in January 1970. One of the many reasons for this was the development costs that were getting out of hand. Another was technical problems, as the technology available at that time was not yet sufficiently advanced to fully meet the ambitious requirements. In addition, the development work repeatedly revealed a lack of willingness on the American side to cooperate consistently.
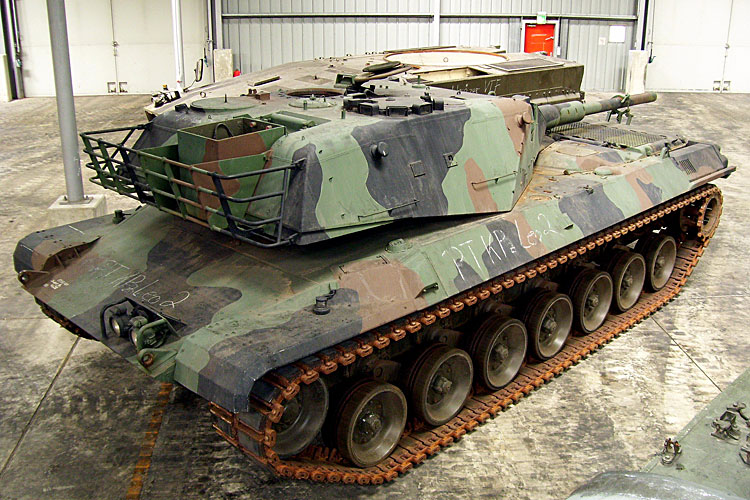

Experimental Entwicklung ~ Experimental Development
The agreement on the development of the Battle Tank 70 prohibited a parallel national battle tank development. However, when there were major tensions in the cooperation with the Americans, the development of a successor for the M48 began again on a purely national level on the German side.
Subsequently, the so-called Experimental Entwicklung (i.e. Development) project was initiated in 1968. The official goal of the programme was to develop components for upgrading of the Leopard 1 in order to increase its combat value to a level close to that of the Main Battle Tank 70. Furthermore, components were to be developed within the scope of the Experimental Entwicklung, which could serve as a basis for a new main battle tank development after the failure of the development of the MBT 70. General contractor for the Experimental Entwicklung was Krauss-Maffei Wehrtechnik GmbH in Munich, Porsche was responsible for the chassis development and Wegmann & Co Gmbh for the turret.
In 1969, two test vehicles were built as part of the programme and handed over to the German Armed Forces in 1970. These were designated ET 1 and ET 2, but are often also referred to as Prototype 1 (PT 1) and 2 (PT 2). The vehicles had a conventional layout, resembled the Leopard 1 optically in many areas, had a 105 mm main gun, a turret featuring spaced armour construction and a weapon station on the turret roof, and were powered by a 10-cylinder Daimler-Benz MB872 diesel engine with an output of 1,250hp.

[Michael Jerchel † via Carl Schulze]
Eber and Keiler
With the official cancelling of the Main Battle Tank 70 project, a dispute about the future direction of the new German MBT now flared up. One side favoured a national continuation of the development of a technically less sophisticated version of the MBT 70 under the name of Kampfpanzer Eber, while the other side demanded to continue the experimental development as a full-fledged MBT development project, the result of which should be introduced under the name of Kampfpanzer Keiler.
Helmut Schmidt, Minister of Defence from 1969 to 1972, finally decided that the Experimental Entwicklung experimental development should be continued under the name Leopard 2, but equipped with the engine developed by MTU and and transmission developed Renk for the MBT 70. But the disputes were not over yet, and now it was debated whether the new MBT should be equipped with a tank gun or the MGM-51 Shillelagh combination weapon of the MBT 70. There were even supporters for the idea to procure and introduce both variants.
For better differentiation the planned vehicles were referred to as Leopard 2 K (tank gun) and Leopard 2 FK (missile / gun combination weapon). In the end, however, the studies for the Leopard 2 FK were stopped in mid-1970.
© Carl Schulze 2020

To be continued…



















Pingback : Bundeswehr Leopard 2 MBT At 40 ~ Part 2 - Joint Forces News
Pingback : Bundeswehr Leopard 2 MBT At 40 ~ Part 3 - Joint Forces News
Pingback : Bundeswehr Leopard 2 MBT At 40 ~ Part 4 - Joint Forces News
Pingback : Bundeswehr Leopard 2 MBT At 40 ~ Part 5 - Joint Forces News
Pingback : Bundeswehr Leopard 2 MBT At 40 ~ Part 6 - Joint Forces News
Pingback : Leopard 2A7V Main Battle Tank ~ Part 2 | Joint Forces News
Pingback : Leopard 2A7V Verbessert Main Battle Tank ~ Part 1 | Joint Forces News