
In this second part of his new series, photojournalist and military historian Carl Schulze looks back at the Leopard 2 MBT Prototypes and the Austere Version.
~
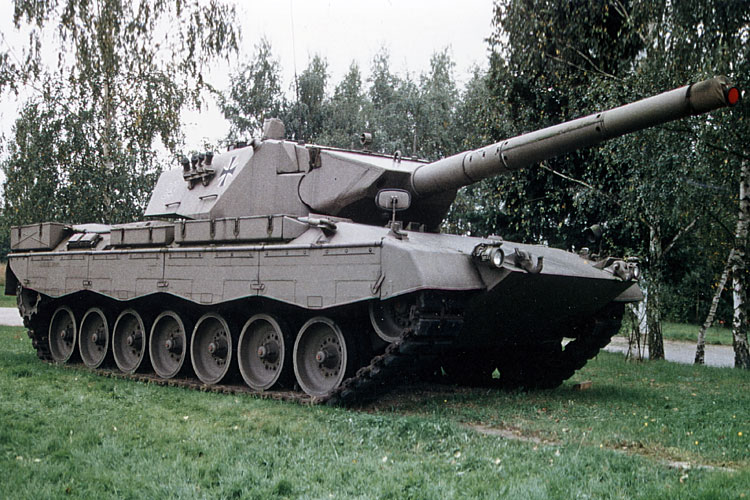
Leopard 2 Prototypes: Between 1972 and 1974, a total of 16 prototype chassis and 17 prototype turrets of the Leopard 2 were built and intensively tested. These prototypes resembled the Leopard 1A4, the last series-produced version of the Leopard 1, in many ways but the individual chassis and turrets of the prototypes often differed significantly in many technical aspects.

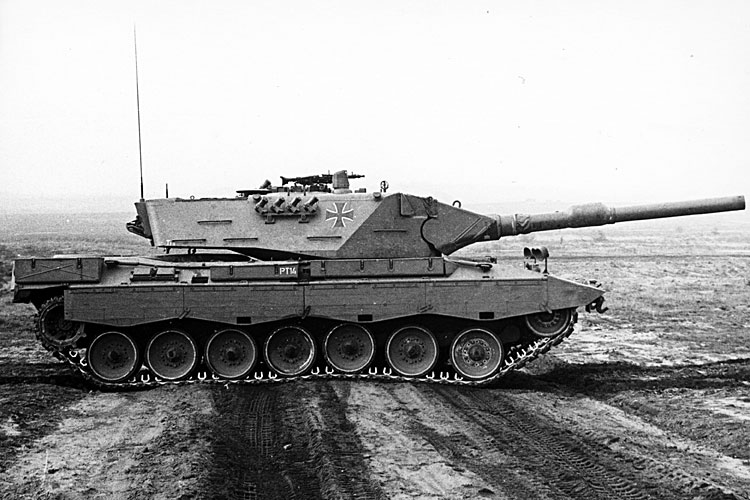
Most of the prototype chassis had torsion bar suspension, while two vehicles were equipped with a hydro-pneumatic suspension. Forged and cast return rollers were used as well as two different types of auxiliary power generator. Some turrets were equipped with a 105mm smoothbore gun, featuring different recoil systems, and some were fitted with a 120mm smoothbore gun with loading aid; all guns being manufactured by the Rheinmetall AG. One turret was fitted with an overhead weapon station that featured a 20mm automatic cannon, serving as secondary armament of the vehicle. The fire control system of all prototypes included the optical, secondarily stabilised range finder EMES 12, a passive night vision device and the commander’s panoramic periscope PERI R12. However, different turret sights were installed, such as the FERO Z12 A1 with night vision eyepiece or the TZF 1A.

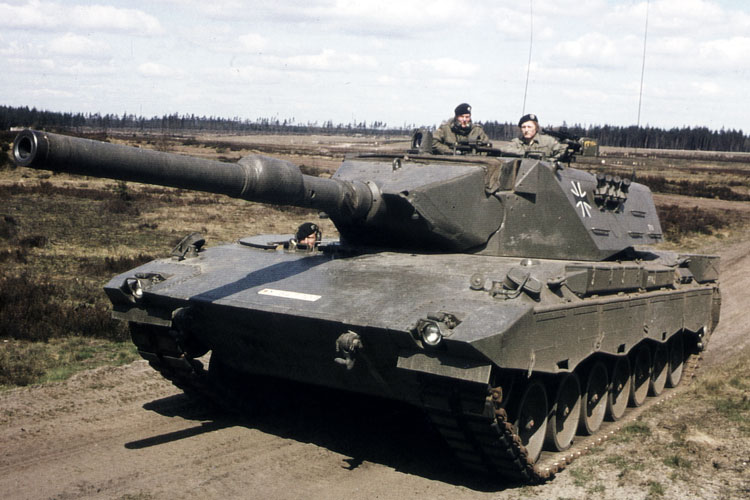
With delivery of the first prototypes, the technical testing of the new main battle tank began, followed by troop trials. The technical trials were carried out, among other places, at the Erprobungsstelle 41 test facility in Trier, the Erprobungsstelle 81 test facility in Greding and the Erprobungsstelle 91 in Meppen. Troop trials were carried out at the Kampf Truppen Schule armoured forces training centre in Munster. A climate zone test under extreme winter temperatures was carried out in Shilo in Canada in winter and in summer under extreme heat in the Yuma Desert in Arizona in the USA.

[© Fachmedien Zentrum Panzer Truppen Schule]
In the course of the tests it became apparent that the prototypes had a significantly higher performance potential than the Leopard 1, but that the technical development status of the hydro-pneumatic suspension was not sufficient for series production. The overhead weapon station with 20mm automatic cannon was not approved either. In regard to the vehicles’ main weapon, the Rheinmetall 120mm smooth-bore gun Rh-120 L/44 won the race. The loading aid was not approved for service, as it did not produce the desired increase in the rate of fire as planned. There were problems with the hard chrome plating of the inner surface of the barrel of the gun and the partially combustible case of the ammunition for the gun. A major problem was also the vehicle weight, which was 1.5 tons above the required Military Load Classification 50 (MLC).
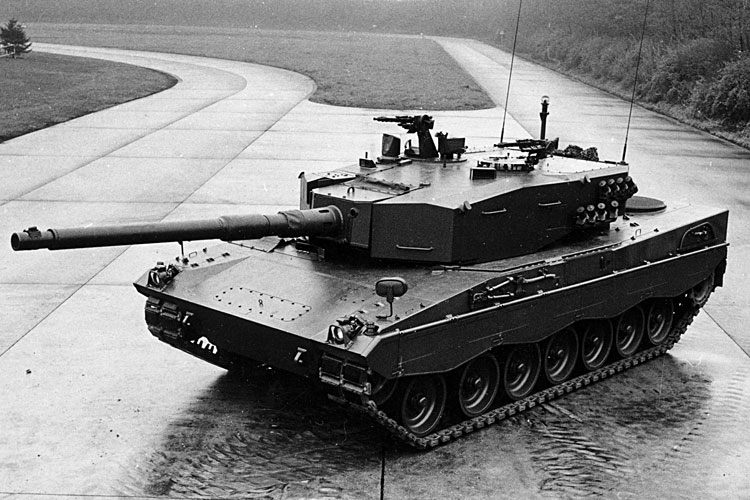

Leopard 2AV: Events in the years 1973 and 1974 were to have a major impact on the further development of the Leopard 2.
Findings from the Yom Kippur War between Egypt, Syria and other Arab states on one side and Israel on the other, showed how vulnerable main battle tanks were to modern anti-tank weapons. As a conclusion, armour protection was now given more priority during the development work.
Due to the lack of budgetary funds, plans to upgrade the Leopard 1 with components from the Leopard 2 development were dropped. As a result of this taking in account the shape of the turret of the Leopard 1 during development of the Leopard 2 no longer had to be considered.
At the political level, there was a renewed rapprochement with the USA in the area of tank development and procurement, which led to a Memorandum of Understanding on the evaluation of the tank concepts planned by both countries with the aim being to introduce the same MBT. At a later stage, the objective of the memorandum was reduced to a harmonisation in certain technological areas of the new battle tanks of both nations, by employing of the same components. One part of the agreement provided that a Leopard 2 was to be made available to the USA at the end of 1976 for comparative testing with a prototype of the XM1.
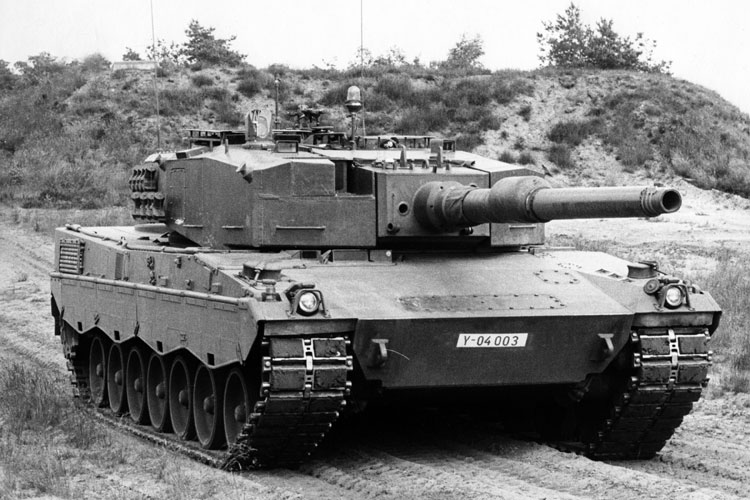

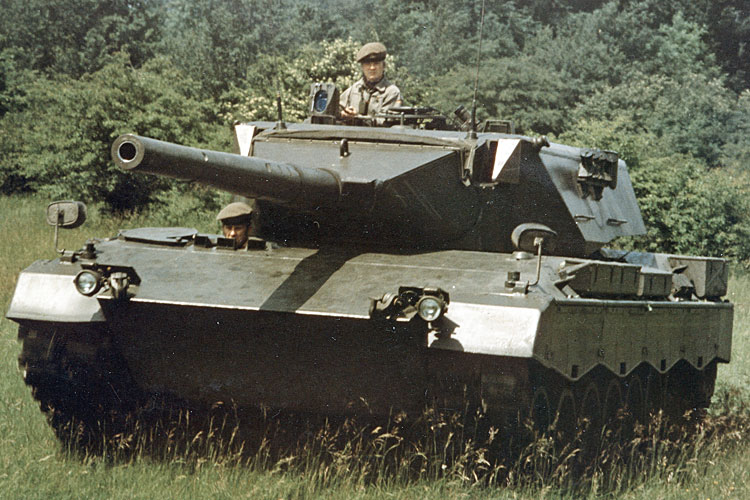
As a result of all these events, Krauss-Maffei Wehrtechnik GmbH was commissioned to develop the Leopard 2AV (Austere Version), which was also to meet all American requirements for a new MBT. Two chassis and three turrets of the Leopard 2AV were built in 1976. These vehicles were equipped with the rifled 105mm gun of the Leopard 1, as the XM1 also had a 105mm gun, but they could be converted and equipped with the 120mm Rh-120 L/44 smoothbore gun. The vehicles featured increased armour protection at the front and sides of turret and hull, and their weight was kept below the limit of MLC 60. The fire control system of the Leopard 2AV was much simpler than that of the earlier prototypes and had a primary stabilised gunner’s sight, which was followed by the main gun.
Comparative testing of the Leopard 2AV in the USA took place at the Aberdeen Proving Ground in Maryland until March 1977. From an American point of view, the Leopard 2AV and the XM1 were equal in firepower and manoeuvrability, but the armour protection of the German product was regarded to be insufficient. After the end of the tests, one of the three turrets remained in the USA, was converted to the 120mm smoothbore gun and was tested intensively on a Leopard 2 prototype chassis that had already been delivered to the USA some time before.
In the long term, the only measurable result of the harmonisation efforts remained the fact that the Rheinmetall 120mm smoothbore gun Rh-120 L/44 was introduced by the USA for the M1 Abrams main battle tank from the M1A1 variant onwards. This weapon is manufactured under licence by General Dynamics Land Systems and is designated M256 120mm Tank Cannon by the US Army.
To be continued…
~



















Pingback : Bundeswehr Leopard 2 MBT At 40 ~ Part 1 - Joint Forces News
Pingback : Bundeswehr Leopard 2 MBT At 40 ~ Part 3 - Joint Forces News
Pingback : Bundeswehr Leopard 2 MBT At 40 ~ Part 5 - Joint Forces News
Pingback : Bundeswehr Leopard 2 MBT At 40 ~ Part 4 - Joint Forces News
Pingback : Bundeswehr Leopard 2 MBT At 40 ~ Part 6 - Joint Forces News