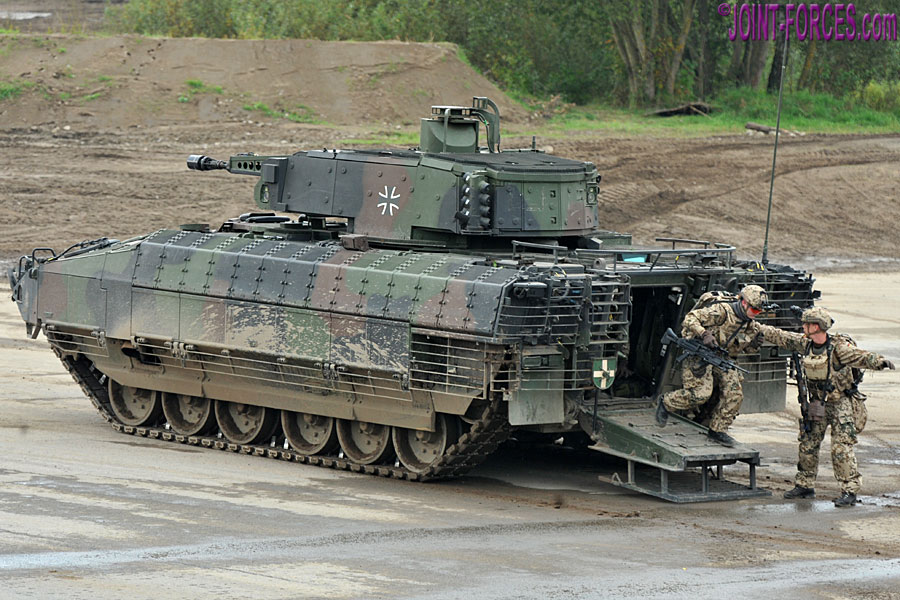

In Part Two of this feature on the Schützenpanzer Puma AIFV we look at the 1.Los (1st Batch) and VJTF variant vehicles in Bundeswehr service, writes Carl Schulze.
~
The SPz Puma 1.Los , or 1st Batch, vehicles were issued to the following five armoured infantry units: Panzergrenadier Lehr Bataillon 92 based in Munster, Panzergrenadier Bataillon 33 based in Neustadt am Rübenberge, Panzergrenadier Bataillon 112 based in Regen, Panzergrenadier Bataillon 122 based in Oberviechtach and Panzergrenadier Bataillon 212 based in Augustdorf. Each of the units received 44 vehicles, with the remainder issued to training establishments such as the Panzertruppenschule.

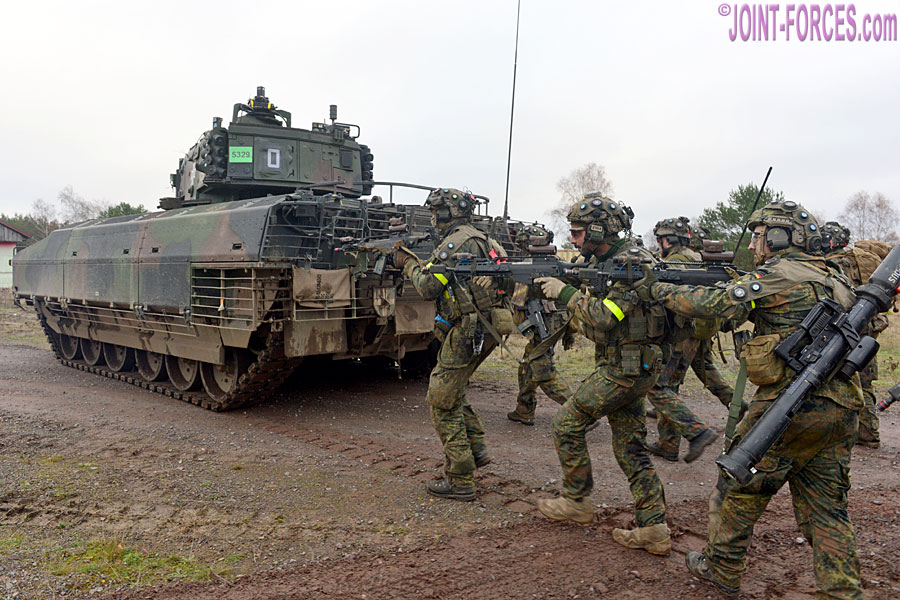
Within the five battalions the SPz Puma is fielded in different configurations that differ mainly by the installed types and numbers of radios. These are namely: the infantry section vehicle; the platoon commander and platoon 2IC vehicle; the company commander vehicle; and the battalion command vehicle variants. Together with the SPz Puma these units were issued with the Infanterist der Zukunft – Erweitertes System Panzergrenadiere (IdZ -ES PzGren) enhanced future soldier system in the armoured infantry configuration; the SPz Puma and the IdZ – ES PzGren together forming the system of systems known as System Panzergrenadier. This allows communications and information exchange between the vehicle crew and the dismounts and by doing so massively enhances situational awareness and command and control.
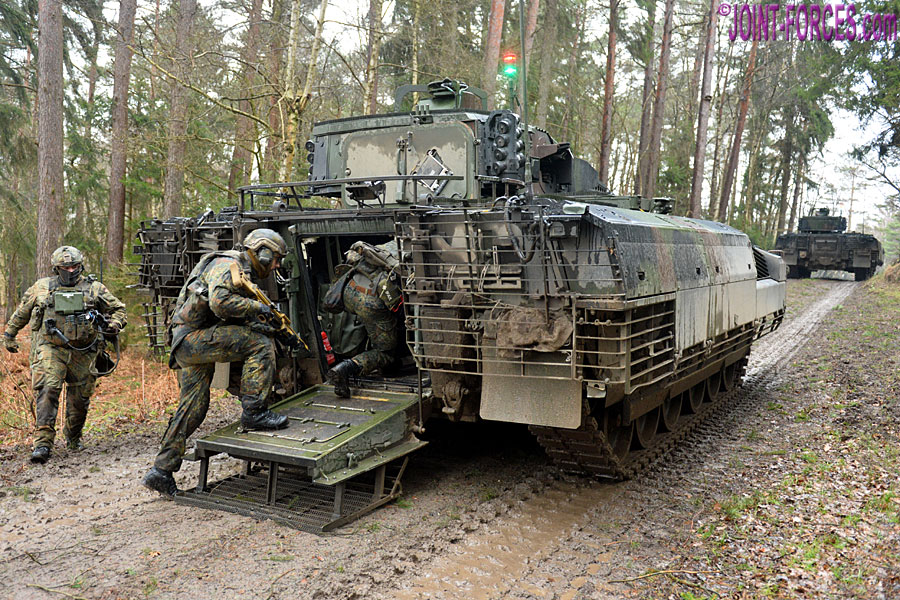

The SPz Puma 1.Los vehicles were not, however, to combat ready status and could only be used for training purposes. One reason for this was that certain components, such as the launcher for the MELLS (Mehrrollenfähiges Leichtes Lenkflugkörpersystem) anti-tank guided missile system and the TSWA (Turmunabhängige Sekundärwaffenanlage) rear mounted secondary armament system had not yet been developed to series production standard. Another reason was various teething troubles, such as technical issues with the vehicle electronics, that caused countless breakdowns. Most likely these technical issues are the result of the extreme complexity of the modern AIFV twinned with its high level of digitalisation.
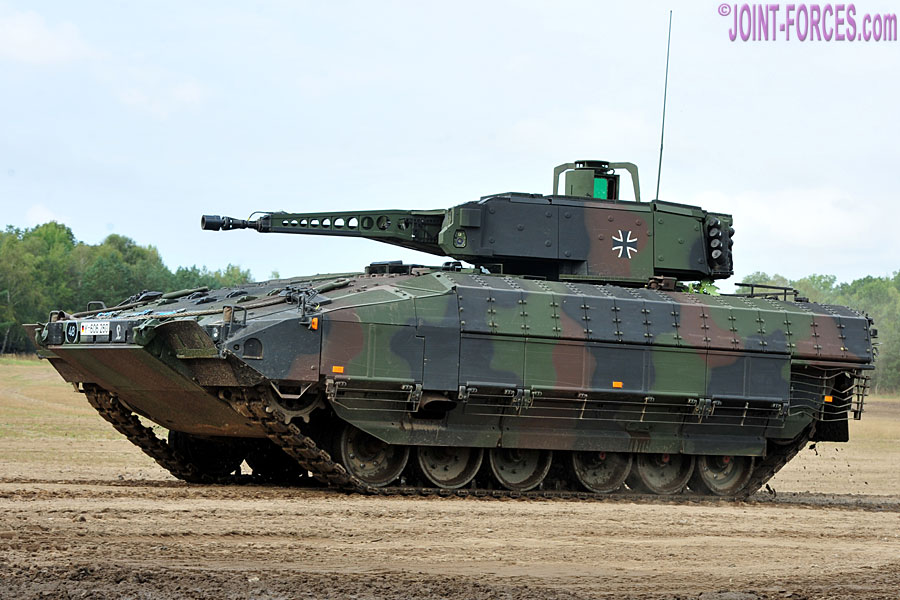

Schützenpanzer Puma VJTF
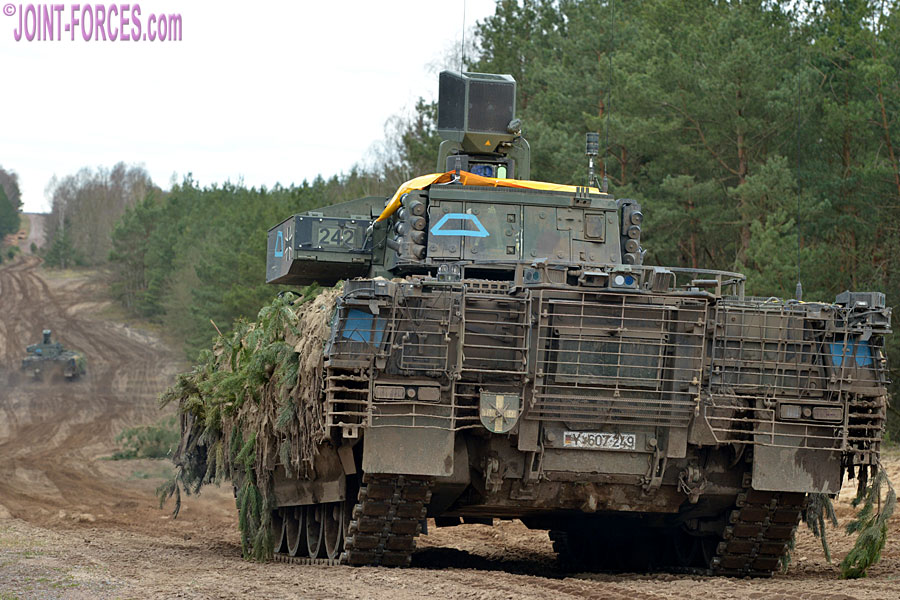
With the German Panzergrenadier Brigade 37 being earmarked to provide the core of the Very High Readiness Joint Task Force (VJTF) of the NATO Response Force (NRF) in 2023, it was imperative to upgrade at least the number of SPz Pumas needed to equip two armoured infantry companies to a state of full operational readiness. Therefore in July 2019 the upgrade of 40 SPz Puma 1.Los into SPz Puma VJTF was ordered. The only unit to receive these improved vehicles was Panzergrenadier Bataillon 112 based in Regen, with deliveries taking place between December 2020 and late 2021. In February 2021 the SPz Puma VJTF underwent tactical user trials conducted at the Bergen-Hohne Training Area and on 12th March 2021 it was declared combat ready.
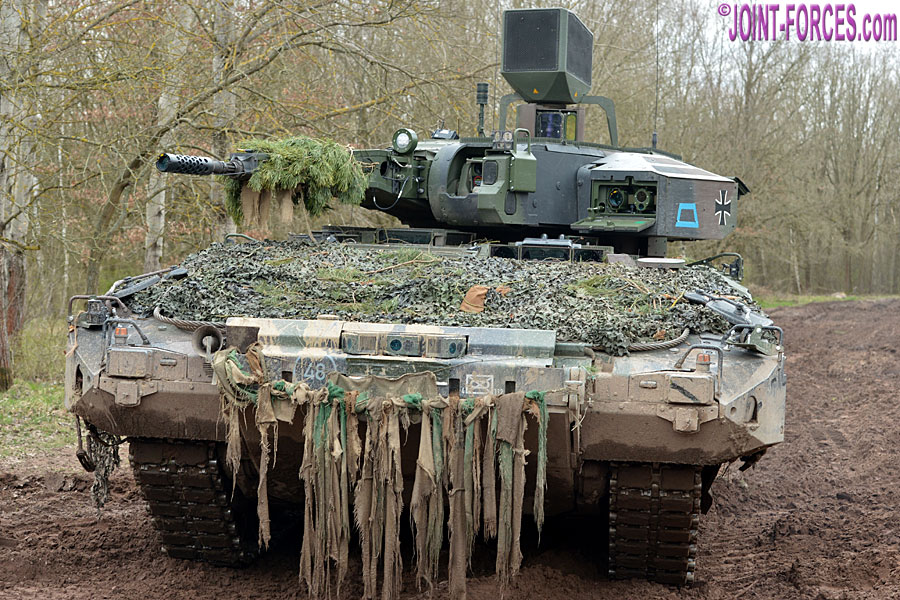

The SPz Puma VJTF features many upgrades and reliability improvements. Main features are the installation of the launcher for the MELLS (Mehrrollenfähiges Leichtes Lenkflugkörpersystem) anti-tank guided missile system on the left turret side, new colour optics and monitors for the gunner and vehicle commander and improved command and control equipment, including new radios.

Schützenpanzer Puma S1
On 28th June 2021 the BAAINBw contracted for the upgrade of 154 SPz Puma 1.Los into SPz Puma S1, basically giving them Full Operational Capability (FOC) ~ roughly equating to what the British Army would call Theatre Entry Standard or TES. This contract included an option for another 143 vehicles and fielding of these was planned for the near future. The SPz Puma S1 standard will be similar to that of the SPz Puma VJTF and also features the MELLS ATGM launcher. It will, however, feature different digital radios that will enter service with the Bundeswehr under the project Digitalisierung – Landbasierter Operationen (D – LBO, digitalisation of land based operations). It will also be prepared for the installation of the Turmunabhängige Sekundärwaffenanlage (TSWA) rear mounted secondary armament system that is still under development.

Puma Project At A Crucial Milestone
Initially it was planned to procure a second batch of 229 SPz Puma. Due to plans for a new structure for the German Army, which instead of an airborne division and two equally structured armoured divisions will now consist of a light division, a medium division and a heavy division, this total has been adjusted several times. Currently it looks like the second batch will only consist of 50 vehicles.
The procurement contract for these was planned to be signed in early 2023. However currently the procurement of the second batch is put on hold, as during an exercise held at the Bergen-Hohne Training Area in early December 2022 over a period of just two weeks 18 out of 18 deployed SPz Puma VJTF of Panzergrenadier Bataillon 112 broke down. At the time of writing, just before Christmas 2022, investigations are being conducted in order to find out why these vehicles broke down.

In a statement the German Defence Minister Christine Lambrecht declared the following about the future of the Puma: “The recent failures of the SPz Puma are a major setback. I ordered the involved departments of the Ministry of Defence, the Bundeswehr, Heeresinstandsetzungslogistik GmbH and the industry to come back to me within one week with a full analysis. The Puma project is at a crucial milestone and I made that absolutely clear to everyone involved. There will be no second production batch until the vehicle proves to be stable.”

Schützenpanzer Puma VJTF Technical Data
- Gross weight: 43 tonnes
- Military Load Class (MLC): 48
- Crew: 9, consisting of commander, gunner, driver and six dismounts
- Length: 7,624mm
- Width: 4,324m
- Height over IR jammer: 3,621mm
- Ground clearance: 450mmm
- Trench crossing: 2.5m
- Fording: 1.2m
- Deep fording without preparation: 1.5m
- Deep fording with fording kit: 1.8m
- Gradient: 60%
- Side slope: 30%
- Top speed on roads: 70km/h
- Maximum range on roads: 550km
- Main armament: 30mm MK30-2/ABM automatic cannon manufactured by Rheinmetall Waffen und Munition GmbH; the gun features a maximum effective range of 3,000m, has a rate of fire of 200 rounds per minute and can fire 30mm x 173 air-burst ammunition ~ 361 round for the gun are carried on the vehicle
- Secondary armament: 5.56mm x 45 MG4 machine gun manufactured by the Heckler & Koch GmbH; the gun features a maximum effective range of 1,000m and has a rate of fire of 950 rounds per minute ~ 2,000 rounds for the weapon are carried on the vehicle
- Missile system: Launcher for two missiles of the Mehrrollenfähiges Leichtes Lenkflugkörpersystem (MELLS) anti-tank guided missile system; manufactured by EuroSpike GmbH the variant of the Spike Long Range missile has an effective range of 4,000m ~ the combat load of the vehicle includes a total of two MELLS missiles.
- Fire control and sighting equipment: Hensoldt AG panoramic periscope featuring a day sight, an ATTICA thermal sight and an LDM 38 laser range finder and Hensoldt AG gunner’s sight featuring a day sight, an ATTICA thermal sight and an LDM 38 laser range finder.
- Protection concept: Modular, including passive armour, enhanced protection bar armour, explosive reactive armour and roof mounted bomblet protection.
- Active-protection system: Multifunktionales Softkill System (MUSS) active self-protection system, consisting of a central electronic unit, a control unit, four sensor heads, an IR jammer and two adjustable smoke grenade launchers with four launch tubes each.
- Engine: MTU Friedrichshafen 10-cylinder MT892Ka-501-A four-stroke turbocharged intercooled direct injection diesel engine developing an output of 800kW.
- Transmission: Renk HSWL 256 hydromatic shifting, reversing and steering transmission with six forward and four reverse gears.
- Running gear: Decoupled from hull and fitted to running gear carriers, consisting on each side of a front mounted drive sprocket, six pairs of road wheels, a rear mounted idler wheel, three support rollers and a track tensioner. The suspension is of the hydrop type and features on each side six hydrop components with end stop dampers and trailing arms. The running gear carriers incorporate a total of six fuel tanks that can accommodate 900 litres of Diesel fuel.
- Other systems: NBC protection system, fire-extinguishing system in power pack compartment and fighting compartment using DeuGenN agent, all around optronic surveillance system featuring a total of eleven wide angle and uncooled thermal cameras and vehicle navigation system consisting of the Honeywell Aerospace Talin 500 internal navigation unit and a Rockwell Collins Explosion Resistant GPS Receiver (ERGR).

¤ Note: Some compound German terms have been broken down.
[images © Carl Schulze]
~
See also:-
- Bundeswehr Schützenpanzer Puma AIFV ~ Part One
- Bundeswehr Schützenpanzer Puma AIFV ~ Part Two
- Bundeswehr VJTF SPz Puma Reliability Problems]
<>



















Pingback : Bundeswehr Schützenpanzer Puma AIFV ~ Part One | Joint Forces News
Pingback : Latest Status of the Schützenpanzer Puma | Joint Forces News