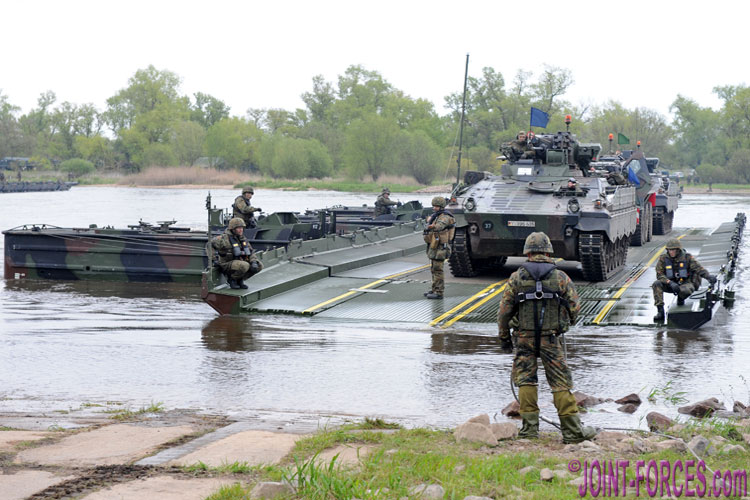

The Improved Ribbon Bridge family of modular flotation bridge systems is a NATO wet-gap crossing asset evolved from a 1960s Soviet design, writes Carl Schulze.
The original Standard Ribbon Bridge (SRB), also called Improved Float Bridge (IFB) by the US Armed Forces, the Faltschwimmbrücke Typ 2 (FSB 2) and the more modern Improved Ribbon Bridge (IRB) flotation bridge systems are wet-gap crossing assets of modular design. Basically a bridging set consists of bridge bay transporters, interior bays and ramp bays, as well as bridge erection boats (BEB). The interior bays and ramp bays can be used to build multi-bay ferries of different sizes or to construct floating bridges of any required length.

A Czech T-72M4 CZ main battle tank crosses a licence-built PMS copy of the Russian PMP ribbon bridge [© Martin Smisek]
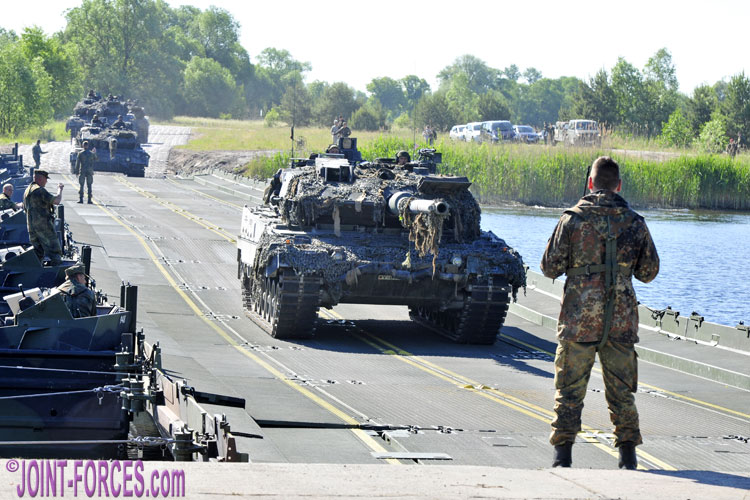

Leopard 2A6 main battle tanks cross a Faltschwimmbrücke Typ 2 (FSB 2) bridge during an exercise held in 2015 [© Carl Schulze]
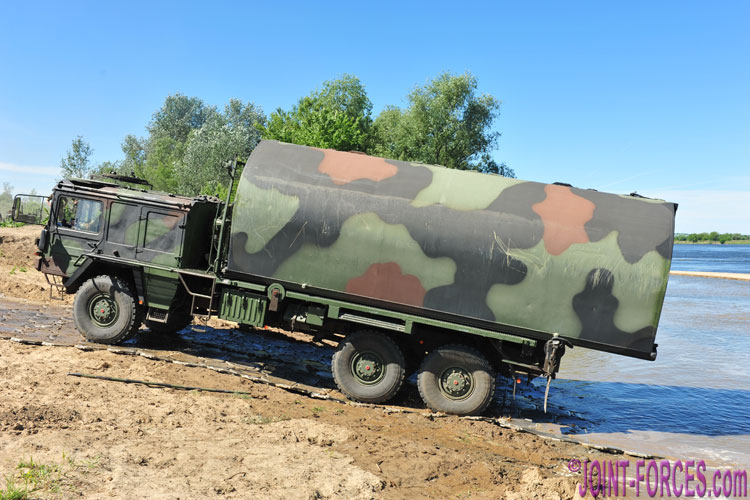

Within the German Army the ramp and interior bays of the Faltschwimmbrücke Typ 2 (FSB 2) are transported by the MAN 7-ton 6×6 KAT 1 Brückentransporter [© Carl Schulze]
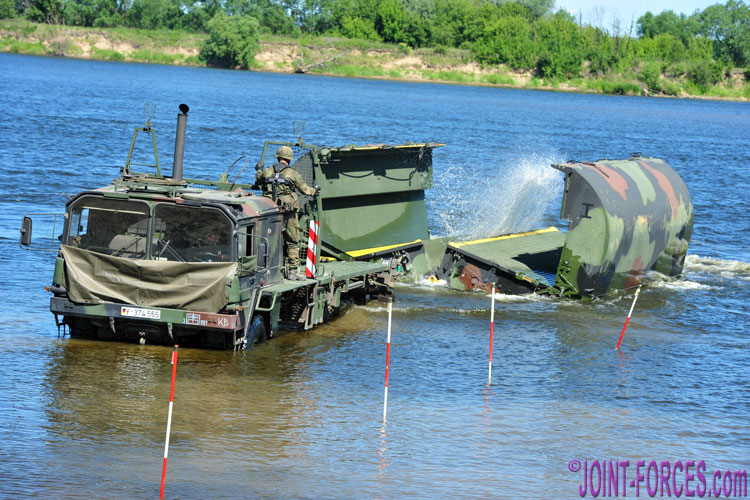

An interior bay of the German Faltschwimmbrücke Typ 2 (FSB 2) bridge unfolds automatically after being launched by a MAN 7-ton 6×6 KAT 1 Brückentransporter [© Carl Schulze]

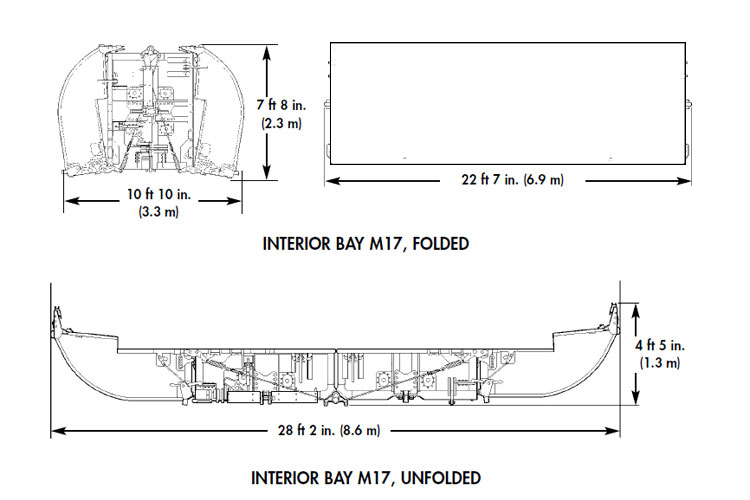
M17 Interior Bay of the Improved Ribbon Bridge (IRB) in service with the US Army after launched – the interior bay has a total weight of 6,350kg [© Carl Schulze]
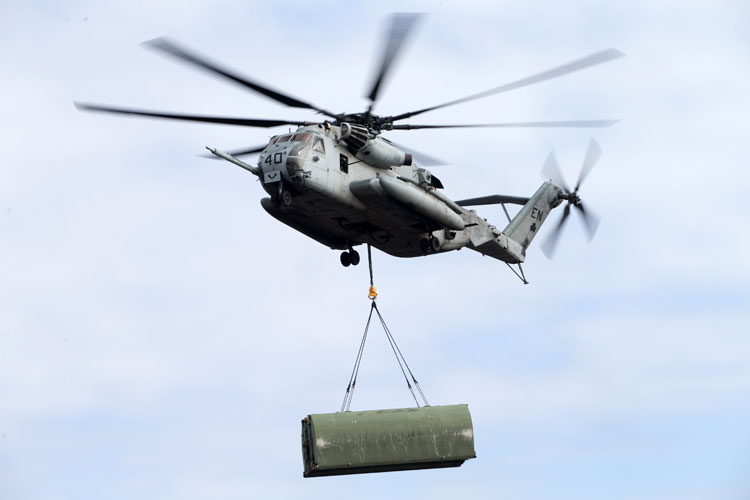

A CH-53E Super Stallion from MHHS 464 deploys a section of an IRB, Camp Lejeune, 15 January 2019 [USMC: LCpl Damion Hatch Jr]
The US Army and the USMC used the IRB several times during Operation IRAQI FREEDOM in Iraq, for example to establish a 523metre long bridge over the Tigris River in the vicinity of Tikrit. In 2015 Australia and Sweden placed orders with GDELS for the IRB system.
To be continued…
{ images © Carl Schulze unless noted }




















Pingback : Delivery of GDELS Floating Bridges to Netherlands | Joint Forces News